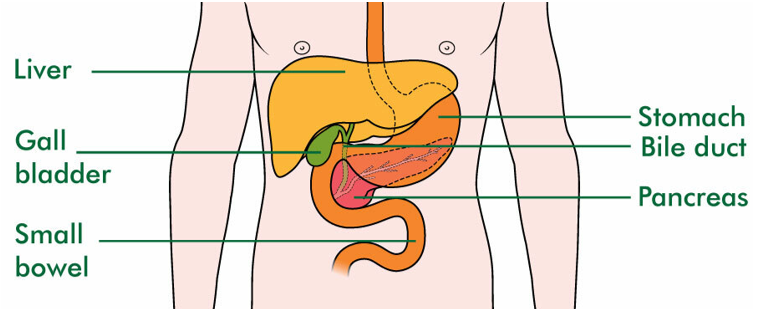
The gallbladder is a small pouch that stores bile. Bile is a fluid that helps us digest food and break down fats. It is made by the liver and stored in the gallbladder. A tube called the bile duct connects the gallbladder to the small intestine and the liver.
Gall bladder cancer is rare, just under 1000 people are diagnosed with it in the UK each year.
Meet the Gastrointestinal (GI) team.
Am I at risk?
Doctors do not know the exact causes of gallbladder cancer. But there are risk factors that can increase your chance of developing it. These are:
- Age
- Sex
- Gallstones and inflammation
- Polyps
- Porcelain gallbladder
- Abnormal bile ducts
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Being overweight
- Family history
- Ethnicity
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)
For more information on the causes of gallbladder cancer, please follow this link.
Symptoms of gallbladder cancer
Early gallbladder cancer does not usually cause symptoms. It is often found when someone has surgery to remove gallstones. But most people who have surgery for gallstones will not have gallbladder cancer.
Most gallbladder cancers are found at an advanced stage. They can cause different symptoms, including:
- sickness
- high temperatures (fevers)
- weight loss
- pain in the tummy (abdomen)
If the cancer blocks the bile duct, it may stop the flow of bile from the gallbladder into the small bowel. This causes bile to flow back into the blood and body tissues. This can cause:
- yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice)
- your pee (urine) to become a dark yellow colour
- pale poo (stools)
- itchy skin
These symptoms may be caused by other problems. But it is important to get them checked by your GP.
For more information on the symptoms of gallbladder cancer, please follow this link.
Patient information
For more information from Macmillan regarding gallbladder cancer, please follow this link.
For more information from Cancer Research UK regarding gallbladder cancer, please follow this link.